06About feline chronic kidney disease
What is chronic kidney disease (CKD)?
- Definition of CKD: Presence of structural or functional abnormalities of one or both kidneys that have been present for an extended period.
- It is the most frequent cause of death in cats aged over five years. Around 30-40% of cats over the age of 10 are said to suffer from CKD1.
- Tubulointerstitial fibrosis is the lesion best correlated with severity of CKD2,3.
- Tubulointerstitial fibrosis both initiate and perpetuate chronic kidney inflammation, hypoxia, and reduced blood flow, ultimately contributing to the irreversible progression of CKD4,5.
Changes in kidney structure
Histology (HE stain*)
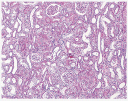
Kidney of a healthy cat
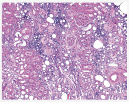
Kidney of a cat with CKD
- Tubulointerstitial fibrosis and inflammation is commonly found in kidney of cats with CKD.
- *HE Stain: Hematoxylin and Eosin stain
Material courtesy of Professor Kenji Ochiai,
Department of Veterinary Pathology,
Faculty of Agriculture, Iwate University
Transmission electron microscopy image
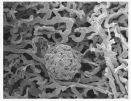
Kidney of a healthy rat
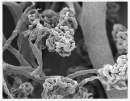
Kidney of a nephritis induction model rat
- There is marked decrease in the capillary network.
- Reprinted from Prostaglandins & other Lipid Mediators 112, Yasufumi Goto, Shinichi Yamaguchi, Mitsutaka Tamura, Hidenori Mochizuki, Hajimu Kurumatani, Kiyoshi Okano, Mitsuko Miyamoto, A prostacyclin analog prevents the regression of renal microvascular network by inhibiting mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in the kidney of rat progressive glomerulonephritis, 16-26., Copyright (2014 Aug), with permission from Elsevier.
Changes in renal function
- Decrease in GFR
- Decreased urinary concentrating ability.
- Decreased ability to adjust electrolytes.
- Decreased hormone secretion capacity, etc.
By the time clinical signs such as loss of appetite, weight loss, decreased energy, polydipsia are seen, it is said that around only 30% of the kidney is still functioning.
Test items
- Blood tests
- ・Serum creatine, blood urea-nitrogen (BUN)
- Urinalysis
- ・Urine protein/creatinine ratio (UPC), urine specific gravity
- Other tests
- ・Blood pressure, ultrasonic exam
and others…
Diagnosis will be made based on these test results, medical history and physical examination.
References
- 1)Sparkes AH, et al. J Feline Med Surg 2016; 18: 219-239.
- 2)Chakrabarti S, et al. Vet Pathol 2013; 50: 147-55
- 3)Yabuki A, et al. Res Vet Sci 2010; 88: 294-299
- 4)Nangaku M. J Am Soc Nephrol 2005; 17: 17-25.
- 5)Fine LG and Norman JT. Kidney Int 2008; 74: 867-872.

